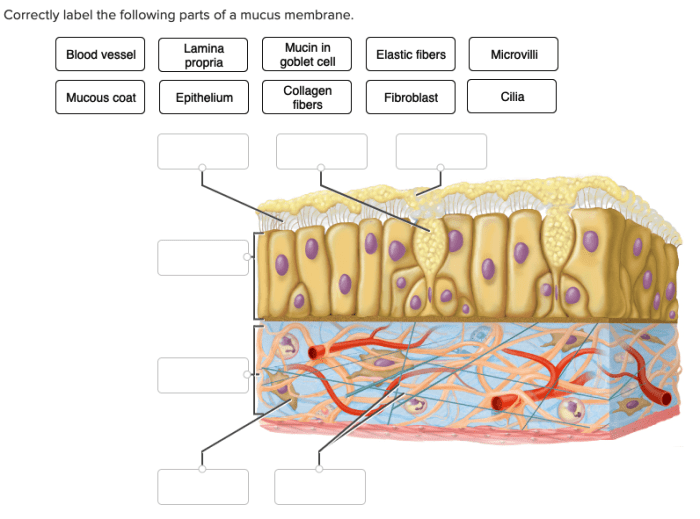
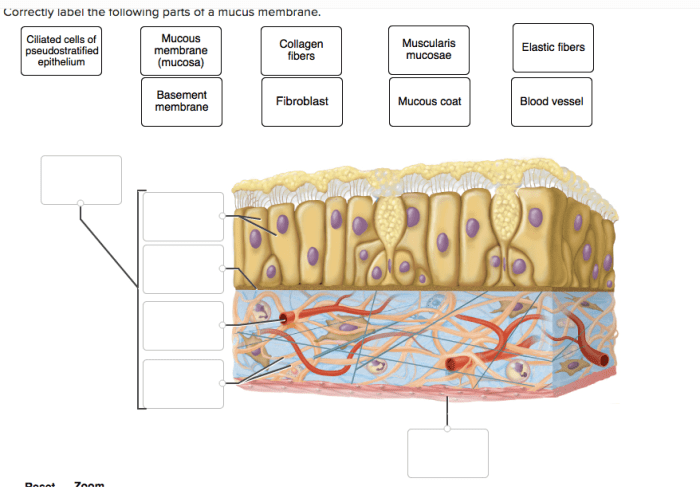
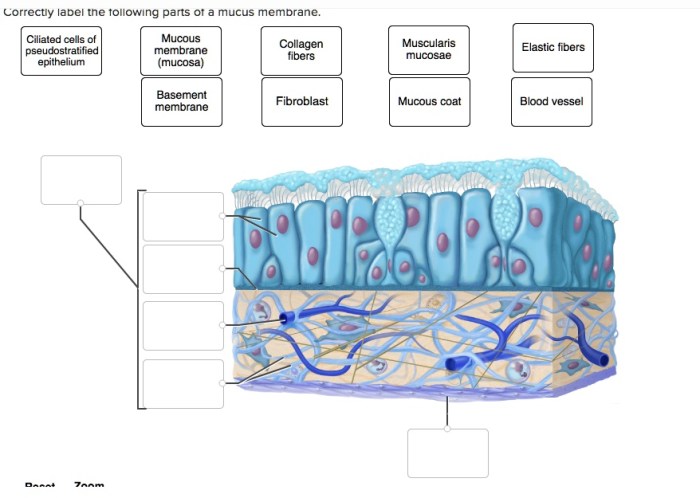
Correctly label the following parts of a mucous membrane. – Correctly labeling the following parts of a mucous membrane is essential for understanding its anatomy and function. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, including a detailed diagram, a discussion of the different types of cells found in a mucous membrane, and a step-by-step guide for correctly labeling its parts.
1.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Mucous Membrane
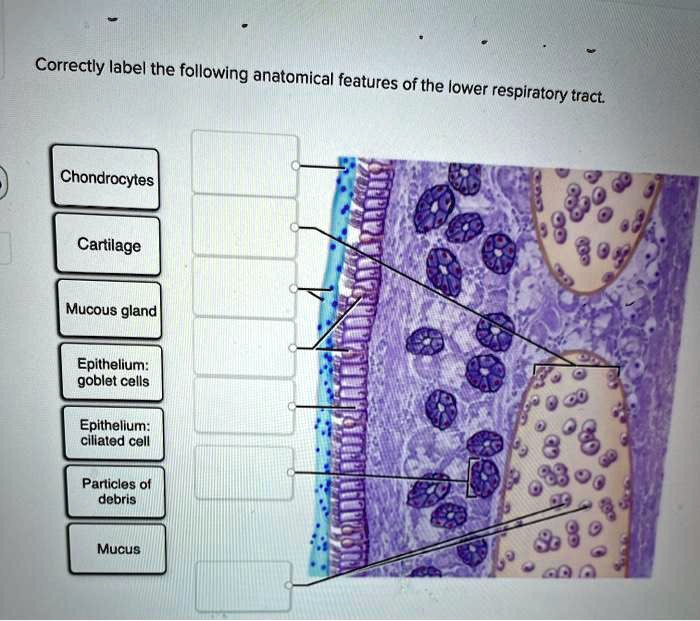
Mucous membranes are specialized tissues that line the body’s cavities and passages that are exposed to the external environment. They serve as a protective barrier against pathogens and facilitate essential functions such as absorption and secretion.
A mucous membrane consists of three main layers:
- Epithelium: The outermost layer, composed of tightly packed cells that form a protective barrier.
- Lamina propria: A connective tissue layer that supports the epithelium and contains blood vessels, nerves, and immune cells.
- Muscularis mucosa: A thin layer of smooth muscle that allows for movement and secretion.
2.
Functions of Mucous Membranes
Mucous membranes play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and protecting the body against harmful substances:
- Protection:The epithelium acts as a physical barrier, preventing pathogens from entering the body. Mucus produced by goblet cells within the epithelium traps and removes pathogens.
- Absorption and secretion:Mucous membranes facilitate the absorption of nutrients and electrolytes, and the secretion of hormones and enzymes.
- pH balance:Mucous membranes help maintain an optimal pH balance by secreting fluids that neutralize acids or bases.
3.
Common Diseases and Disorders of Mucous Membranes
Mucous membranes can be affected by various diseases and disorders:
- Stomatitis:Inflammation of the oral mucous membrane, causing pain, redness, and swelling.
- Sinusitis:Inflammation of the mucous membranes lining the sinuses, leading to congestion, pain, and discharge.
- Bronchitis:Inflammation of the bronchial mucous membranes, causing coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
4.
Clinical Applications of Mucous Membrane Analysis
Examining mucous membranes is an important part of clinical practice:
- Assessment of hydration:Dry, cracked mucous membranes indicate dehydration.
- Diagnosis of anemia:Pale mucous membranes may suggest anemia.
- Detection of jaundice:Yellowish mucous membranes can indicate liver disease.
5.
Techniques for Correctly Labeling Mucous Membrane Parts
Accurate labeling of mucous membrane parts is essential for effective communication:
- Use anatomical landmarks:Identify key structures such as the lips, tongue, and palate.
- Study diagrams and illustrations:Refer to detailed images to visualize the anatomy.
- Practice labeling:Use interactive resources or quizzes to reinforce your understanding.
General Inquiries: Correctly Label The Following Parts Of A Mucous Membrane.
What is the purpose of a mucous membrane?
A mucous membrane is a moist, protective lining that covers the surfaces of the body that are exposed to the external environment. It helps to protect the body from pathogens, regulate pH balance, and facilitate absorption and secretion.
What are the different types of cells found in a mucous membrane?
The different types of cells found in a mucous membrane include epithelial cells, goblet cells, and immune cells. Epithelial cells form the protective barrier of the mucous membrane, goblet cells secrete mucus, and immune cells help to protect the body from infection.
How do I correctly label the parts of a mucous membrane?
To correctly label the parts of a mucous membrane, follow the steps Artikeld in the guide above. This includes identifying the different layers of the mucous membrane, as well as the different types of cells that are found in each layer.