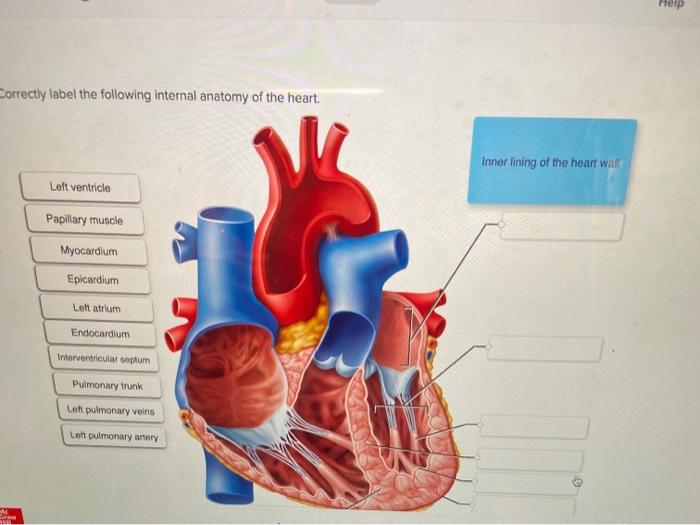
Correctly label the following internal anatomy of the heart. – Correctly labeling the internal anatomy of the heart is crucial for understanding its intricate structure and function. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the heart’s chambers, valves, blood flow, and electrical conduction system, empowering you with the knowledge to accurately identify and describe its components.
The heart, a vital organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, comprises four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The atria receive blood from the body and lungs, while the ventricles pump blood out to the body and lungs.
Valves within the heart, such as the tricuspid and mitral valves, prevent backflow of blood, ensuring proper circulation.
Anatomical Structure of the Heart
The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It consists of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
Chambers of the Heart
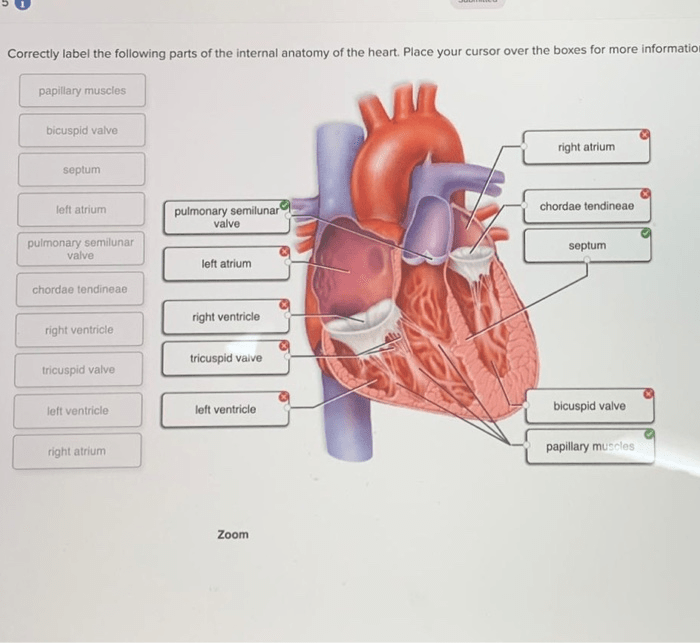
- Atria:The upper chambers of the heart that receive blood from the body and lungs.
- Ventricles:The lower chambers of the heart that pump blood out to the body and lungs.
Pericardium
The pericardium is a sac-like structure that surrounds the heart and provides protection and lubrication.
Endocardium and Myocardium
- Endocardium:The inner lining of the heart that prevents blood leakage.
- Myocardium:The muscular wall of the heart that contracts to pump blood.
Blood Flow through the Heart
Blood enters the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava and flows through the following pathway:
Atrioventricular Valves
- Tricuspid valve:Located between the right atrium and right ventricle, prevents blood from flowing back into the atrium.
- Mitral valve (bicuspid valve):Located between the left atrium and left ventricle, prevents blood from flowing back into the atrium.
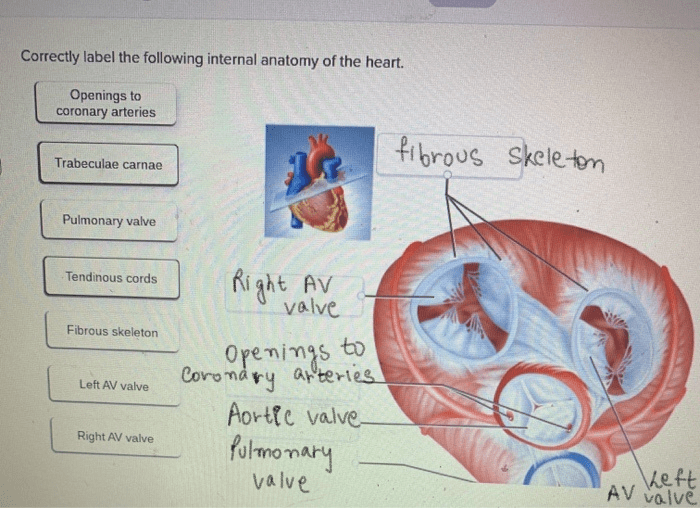
Semilunar Valves, Correctly label the following internal anatomy of the heart.
- Aortic valve:Located at the exit of the left ventricle, prevents blood from flowing back into the ventricle.
- Pulmonary valve:Located at the exit of the right ventricle, prevents blood from flowing back into the ventricle.
Cardiac Cycle
- Systole:When the ventricles contract and pump blood out.
- Diastole:When the ventricles relax and fill with blood.
Electrical Conduction System
The electrical conduction system initiates and coordinates the heart’s contractions:
Components
- Sinoatrial node (SA node):The natural pacemaker of the heart, located in the right atrium.
- Atrioventricular node (AV node):Delays electrical impulses slightly, allowing the atria to fill before the ventricles contract.
- Bundle of His:A group of fibers that transmit impulses from the AV node to the ventricles.
Impulse Propagation
- Impulses originate in the SA node and spread to the atria, causing them to contract.
- Impulses are delayed at the AV node, allowing the atria to fill completely.
- Impulses travel through the bundle of His and cause the ventricles to contract.
Regulation of Heart Function: Correctly Label The Following Internal Anatomy Of The Heart.
Heart rate and blood pressure are regulated by several mechanisms:
Autonomic Nervous System
- Sympathetic nervous system:Increases heart rate and blood pressure.
- Parasympathetic nervous system:Decreases heart rate and blood pressure.
Hormones
- Adrenaline:Increases heart rate and blood pressure.
- Thyroid hormones:Increase the metabolic rate and heart rate.
Baroreceptors and Chemoreceptors
- Baroreceptors:Monitor blood pressure and adjust heart rate and blood pressure accordingly.
- Chemoreceptors:Monitor blood pH and oxygen levels and adjust heart rate and blood pressure accordingly.
Factors Affecting Heart Function
- Exercise
- Stress
- Disease
User Queries
What are the four chambers of the heart?
The four chambers of the heart are the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
What is the function of the pericardium?
The pericardium is a protective sac that surrounds the heart and helps to keep it in place.
What are the atrioventricular valves?
The atrioventricular valves are the tricuspid valve and the mitral valve. They prevent blood from flowing back into the atria when the ventricles contract.