Arterial blood gas nclex questions – Arterial blood gas (ABG) interpretation plays a pivotal role in clinical practice, providing invaluable insights into respiratory and metabolic function. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of ABG analysis, empowering nurses with the knowledge and skills to accurately interpret ABG reports, assess patient status, and guide appropriate interventions.
This guide will thoroughly examine the components of an ABG report, highlighting the significance of pH, PaCO2, and HCO3- levels. We will explore the nuances of ABG sampling techniques, ensuring safe and effective sample collection. Furthermore, we will delve into the clinical applications of ABG analysis, discussing its utility in assessing respiratory and metabolic disorders, guiding ventilator management, and identifying potential pitfalls.
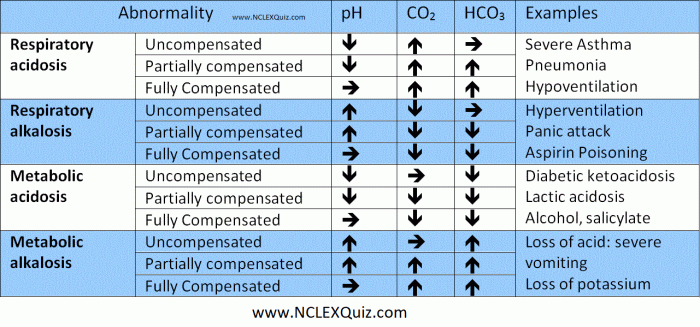
1. Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Interpretation

Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis provides valuable information about the respiratory and metabolic status of a patient. The ABG report includes the following components:
- pH: Measures the acidity or alkalinity of the blood.
- PaCO2: Measures the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood.
- HCO3-: Measures the concentration of bicarbonate ions in the blood.
The normal ranges for these values are as follows:
- pH: 7.35-7.45
- PaCO2: 35-45 mmHg
- HCO3-: 22-26 mEq/L
Deviations from these normal ranges can indicate various respiratory and metabolic disorders.
Metabolic Acidosis and Alkalosis
Metabolic acidosis occurs when there is an excess of acid in the blood or a loss of bicarbonate ions. It can be caused by conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, and renal failure. ABG values that indicate metabolic acidosis include:
- pH:< 7.35
- HCO3-:< 22 mEq/L
Metabolic alkalosis occurs when there is a decrease in acid or an increase in bicarbonate ions in the blood. It can be caused by conditions such as prolonged vomiting, hyperventilation, and hypokalemia. ABG values that indicate metabolic alkalosis include:
- pH: > 7.45
- HCO3-: > 26 mEq/L
Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis, Arterial blood gas nclex questions
Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is an increase in PaCO2 in the blood. It can be caused by conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and pneumonia. ABG values that indicate respiratory acidosis include:
- pH:< 7.35
- PaCO2: > 45 mmHg
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there is a decrease in PaCO2 in the blood. It can be caused by conditions such as hyperventilation, anxiety, and salicylate overdose. ABG values that indicate respiratory alkalosis include:
- pH: > 7.45
- PaCO2:< 35 mmHg
Answers to Common Questions: Arterial Blood Gas Nclex Questions
What are the key components of an ABG report?
pH, PaCO2, HCO3-, SaO2, and base excess
How do you differentiate between respiratory and metabolic acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis is characterized by decreased pH and increased PaCO2, while metabolic acidosis is characterized by decreased pH and decreased HCO3-.
What are the potential complications of ABG sampling?
Bleeding, hematoma formation, nerve damage, and infection