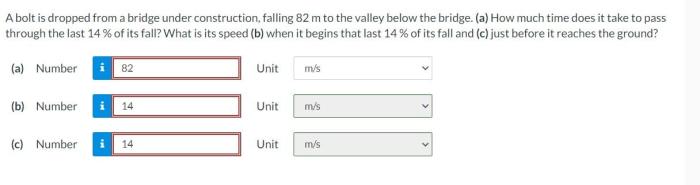
A bolt is dropped from a bridge under construction, setting the stage for this captivating exploration into the realm of physics. As the bolt plummets towards the water below, we embark on a journey that unravels the intricate interplay of free-fall motion, energy conversion, and the effects of air resistance.
This captivating narrative delves into the fundamental principles governing falling objects, examining the factors that influence their acceleration, velocity, and height. We explore the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy, tracing the bolt’s transformation as it falls. The impact of air resistance on the bolt’s trajectory and velocity is meticulously analyzed, revealing the factors that shape its magnitude.
Free-Falling Motion
Free-falling motion refers to the movement of an object solely under the influence of gravity. When an object is dropped, it experiences a constant acceleration due to gravity, known as the acceleration due to gravity (g), which is approximately 9.8 m/s² on Earth.
Factors Affecting Acceleration
The acceleration of a falling object is primarily influenced by:
- Mass of the object:Mass has no effect on the acceleration due to gravity.
- Gravitational field strength:The strength of the gravitational field, which varies depending on the location.
- Air resistance:Air resistance, which can significantly affect the acceleration of an object, especially at higher speeds.
Relationship between Height, Velocity, and Time
In free-fall, the height (h), velocity (v), and time (t) are related by the following equations:
- v = gt
- h = 0.5gt²
- v² = 2gh
Potential and Kinetic Energy: A Bolt Is Dropped From A Bridge Under Construction

Definition
Potential energy (PE)is the energy an object possesses due to its position or height above a reference point. Kinetic energy (KE)is the energy an object possesses due to its motion.
Conversion of Energy
As an object falls, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. The potential energy at the starting point is maximum, and it decreases as the object falls. Simultaneously, the kinetic energy increases as the velocity of the object increases.
Calculating Potential Energy
The potential energy (PE) of the bolt before it is dropped can be calculated using the formula:
PE = mgh
where m is the mass of the bolt, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the initial height from which the bolt is dropped.
Air Resistance
Effects
Air resistance is the force that opposes the motion of an object moving through a fluid, such as air. It acts in the opposite direction of the object’s motion and affects its velocity and acceleration.
Factors Influencing Air Resistance
The magnitude of air resistance depends on several factors:
- Object’s shape and size:Streamlined objects experience less air resistance than irregular-shaped objects.
- Object’s velocity:Air resistance increases significantly with increasing velocity.
- Fluid’s density:Air resistance is greater in denser fluids, such as water, compared to air.
Impact on Bolt
Air resistance affects the bolt’s velocity and acceleration as it falls. Initially, air resistance is negligible, but it becomes more significant as the bolt’s velocity increases. This causes the bolt’s acceleration to decrease and its velocity to reach a terminal velocity, where the force of air resistance balances the force of gravity.
Impact on the Water

Impact Physics, A bolt is dropped from a bridge under construction
When the bolt hits the water’s surface, it creates a splash due to the sudden displacement of water. The impact produces sound waves, which are created by the vibrations of the water’s surface.
Damage
The impact of the bolt on the water can cause damage if the bolt is heavy or has a high velocity. The impact can create a shockwave that can damage underwater structures or harm marine life.
Clarifying Questions
What is free-fall motion?
Free-fall motion refers to the motion of an object falling under the sole influence of gravity, without any other forces acting upon it.
How does air resistance affect a falling object?
Air resistance is a force that opposes the motion of an object moving through the air. It reduces the object’s velocity and acceleration, causing it to reach a terminal velocity.
What factors influence the magnitude of air resistance?
The magnitude of air resistance depends on the object’s shape, size, and velocity, as well as the density of the air through which it is moving.